Have you ever wondered how those vibrant, eye-catching hair colors are achieved? The magic often lies in hair bleach, a powerful chemical process that dramatically alters the natural pigment of your hair. While achieving the perfect shade can seem daunting, understanding the underlying chemistry is key to achieving safe and effective results. From lightening your natural color to preparing for a vibrant dye job, bleach acts as the crucial foundation for countless hair transformations. Many are tempted to try bleaching at home, but it’s important to understand the process fully.
This article provides a comprehensive, step-by-step guide to hair bleaching, outlining the necessary precautions and techniques for achieving successful results. We’ll delve into the chemical reactions involved, explore the different types of bleach available, and importantly, detail the process from preparation to aftercare, ensuring you have all the knowledge needed to safely and effectively bleach your hair. Let's dive into the step-by-step process now.
Preparation and Safety Guidelines
- Hair bleach containing hydrogen peroxide and ammonia
- Always perform a strand test 24-48 hours before bleaching your entire head to check for allergic reactions and see how your hair responds to the bleach.
- Use a low-volume developer (e.g., 10 or 20 volume) for less damage, especially if you are a beginner or have previously damaged hair. Higher volume developers lift faster but cause more damage.
- Never leave bleach on your hair longer than the instructions specify. Over-processing can lead to severe damage, breakage, and scalp irritation.
Step-by-Step Instructions
Understanding the Basics
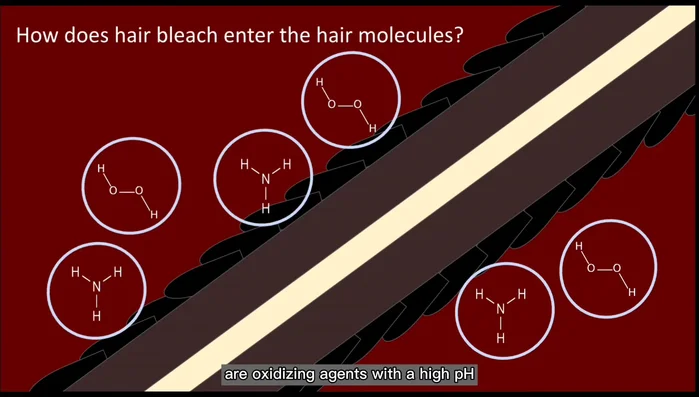
- Hydrogen peroxide and ammonia are the active ingredients, acting as alkaline oxidizing agents.
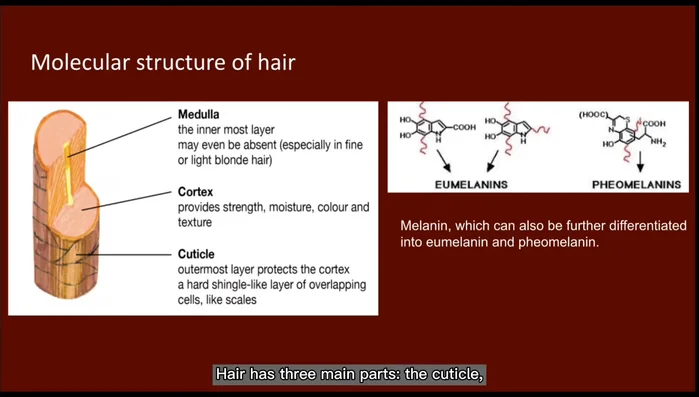
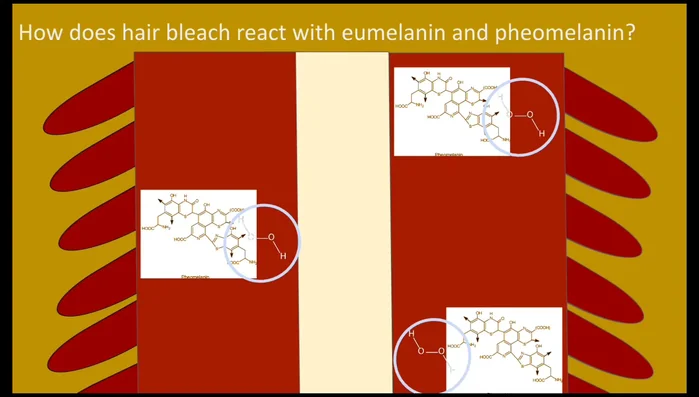
- Hair consists of the cuticle, medulla, and cortex. Melanin pigments (eumelanin and pheomelanin) in the cortex determine hair color.

Understanding the Basics Cuticle Penetration and Swelling
- Hydrogen peroxide and ammonia, with their high pH, permeate the cuticle's cell membranes, causing swelling and creating openings.

Cuticle Penetration and Swelling Melanin Breakdown
- Hydrogen peroxide attacks tyrosinase, a key enzyme in melanin synthesis, by oxidizing an amino acid at its active site, preventing melanin production.
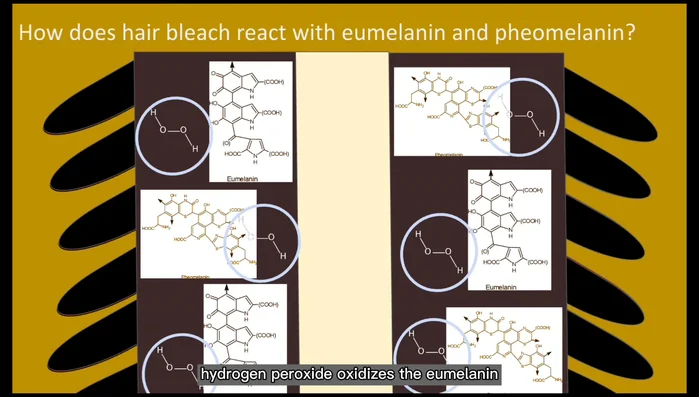
- Hydrogen peroxide oxidizes and dissolves eumelanin (responsible for dark brown color).
- After eumelanin, hydrogen peroxide oxidizes and dissolves pheomelanin (responsible for reddish-brown color).



Melanin Breakdown Final Result
- Only carotene remains, resulting in pale yellow bleached hair.

Final Result
Read more: Super Effective Hair Dye Remover: Baking Soda & Dish Soap Power Wash
Tips
- N/A